Tag: optimal density
What is the process of precision die casting?
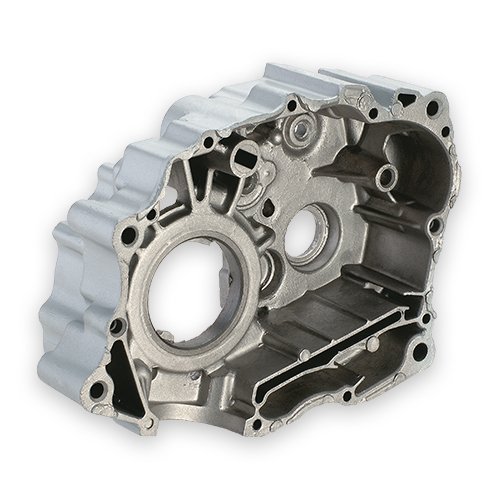
Die casting is a metal casting technique that involves squeezing molten metal into a mould cavity under high pressure. The mould cavity is constructed utilising two hardened tool steel dies that have been machined into shape and function during the process similar to an injection mould. Nonferrous metals, notably zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys, are used to make the majority of die castings. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot-chamber or cold-chamber machine is used. Precision die casting is popular.
Process of die casting
Die casting is a metal casting method in which molten metal is pressed into a steel mould chamber under great pressure. Steel moulds, known as dies, are created to make castings with complicated forms while ensuring precision and reproducibility.
- Hot-chamber die casting is an excellent choice for alloys that do not quickly attack and dissolve metal pots, cylinders, and plungers. It is utilised in the production of zinc, some magnesium alloys, and other low melting alloys.
- Cold-chamber dies casting technique is better suited for metals with high melting points, such as aluminium. Metal is liquefied and then ladled into a cold chamber where a hydraulically driven plunger drives the metal into the die.

Advantages
Because of the die casting process’s versatility and benefits, incorporating it in your next product or component, ornamental trim, and/or final product has several advantages:
- Components are long-lasting and dimensionally stable.
- When compared to other techniques of manufacturing, it can produce complicated forms with tighter tolerances.
- It is capable of combining several functionalities into a single, complexly structured component.
- High output speeds with minimal or no machining.
- Components with thinner walls than those produced by conventional casting processes are possible.
- Much more durable than other plastic injection mouldings.
- Thousands of similar castings can be produced in mass quantities within defined tolerances.
- With minimal surface preparation, zinc castings may be simply plated or polished.
- Smoother surfaces than most alternative casting methods, such as sand or permanent mould.
- Holes can be cored and drilled to specific diameters.
- External threads on pieces can be cast as well.
- Integral fastening features, such as bosses and studs, can be used to save assembly costs.
- Zinc castings are extremely corrosion resistant.
Conclusion
Precision Die Casting is a manufacturing method that pours or injects molten metals into moulds made of steel, compacted sand, and other materials. This enables each item to be made with precision and reproducibility. Die castings have a very excellent surface polish (according to casting standards) and dimensional uniformity.